PROXIMANOVA-LIGHT.OTF PROXIMANOVA-LIGHTIT.OTF PROXIMANOVA-EXTRABLD.OTF PROXIMANOVA-BOLD.OTFPROXIMANOVA-BLACK.OTF
Get this font in here!
This Article Applies to:
- AVG Business Cloud Console
AVG Firewall is another major component of Antivirus protection offered alongside Core Shields, and it is available for Windows workstations. Our Firewall monitors all network traffic between devices and the outside world to help protect you from unauthorized communication and intrusions.
Firewall's advanced packet rules are the final level of Firewall rule evaluation, meaning they are utilized only if the connection does not fit any system or application rules. These rules control whether network traffic is allowed or blocked based on the information contained in network packets. This information may include network protocols, source or destination IP addresses, or local and remote ports. Advanced users can manage these rules or create new ones.
The default packet rules are tied to the
We recommend you only modify these rules if you have advanced knowledge of firewall concepts, as AVG Firewall is already configured to provide the appropriate firewall protection in most cases.
Configuring Advanced Packet Rules
To access advanced packet rules:
- Open the Policies page
- Click the desired policy to open its Detail drawer
- Select the Settings tab, then Firewall
- Expand the Firewall Settings section
- Select the Firewall rules tab, then Advanced packet rules
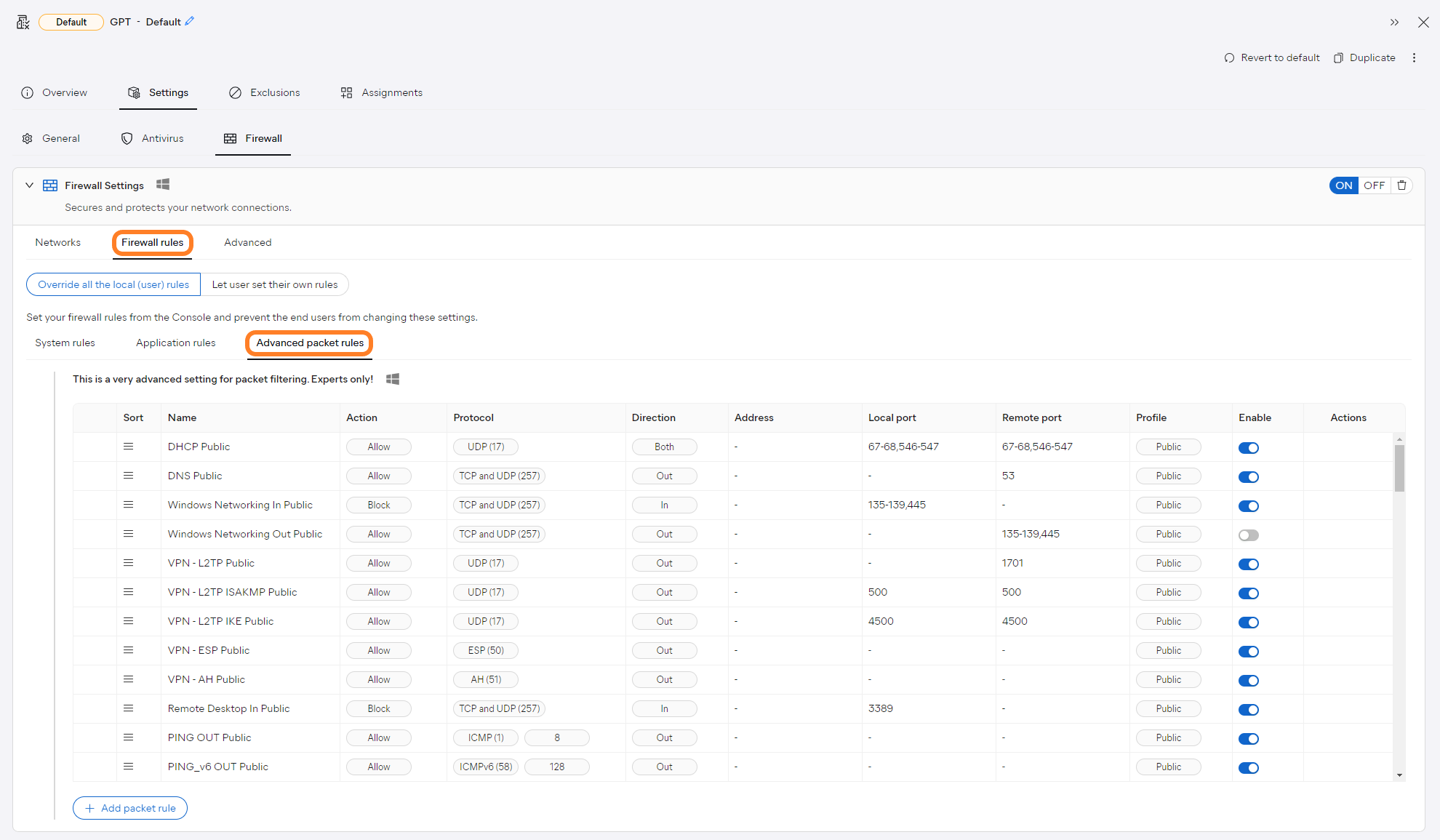
Although you can allow local configuration of all Firewall rules by selecting the Let user set their own rules option at the top of this section, we recommend choosing the Override all the local (user) rules option, ensuring these rules are controlled by your console for maximum security across your network.

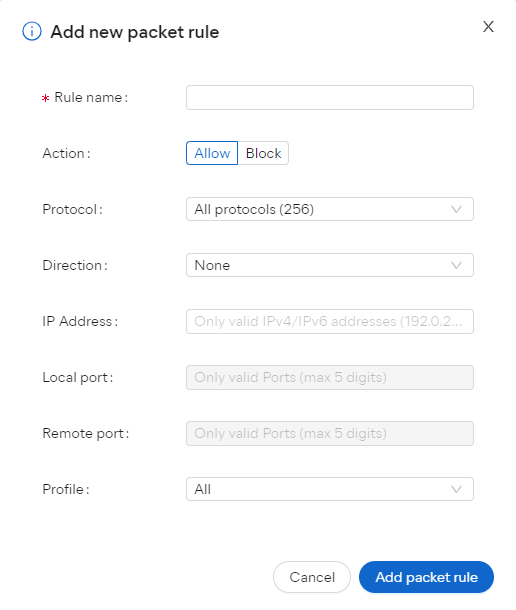
Adding Advanced Packet Rules
To add an advanced packed rule:
- Click the + Add packet rule button at the bottom of the list
- Fill out the following:
- Rule name
- Action: Indicates whether Firewall will Allow or Block the connection
- Protocol: Indicates the network protocol the rule applies to. One protocol may be selected, or All if the rule applies to all protocols.
- If you select Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP/ICMPv6), you will also need to specify the ICMP type, which indicates the control message (represented by a code number) to which the rule applies. The rule may apply to a single code number, or multiple codes (separated by commas). The code numbers of control messages are listed in the technical specifications of the ICMP (RFC 792).
- Direction: Indicates whether the rule applies to incoming connections (In), outgoing connections (Out), or to connections in both directions (Both).
- IP Address: Indicates the source or destination IP address the rule applies to. The rule may apply to a single IP address, multiple IP addresses (separated by commas), or an IP address range (starting with the lowest IP address and separated with a dash). If the field is blank, the rule applies to all IP addresses.
- Local Port: Indicates a network port number on the local IP address of your PC's network interface. The rule may apply for a single port number, multiple ports (separated by commas), or a port range (starting with the lowest port number and separated with a dash). If the field is blank, the rule applies to all local ports.
- Remote Port: Indicates a network port number on the remote IP address of the external server or device. The rule may apply for a single port number, multiple ports (separated by commas), or a port range (starting with the lowest port number and separated with a dash). If the field is blank, the rule applies to all remote ports.
- An application may need to communicate with a specific remote port in order to function. For example, your internet browser usually needs port 443, as this is the default port used for HTTPS (secure HTTP). To verify the remote port that is required by a particular application, contact the application vendor or refer to the application's support pages.
- Profile: Indicates whether the rule applies to Private, Public, or All networks
- Click Add packet rule
The new rule will then be added to the list. You can modify/delete it if needed by clicking the pencil/trash bin icon in the Actions column, or you can enable/disable it by clicking the toggle in the Enable column.
